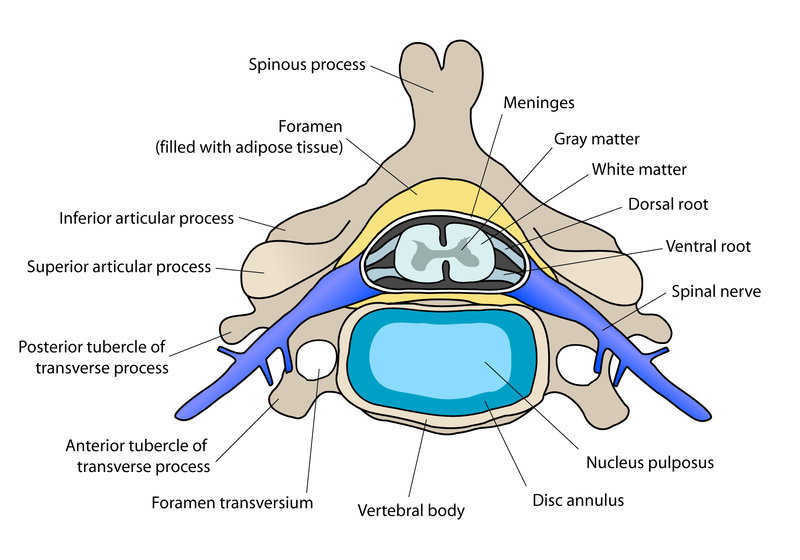
I had stated in a recent post that the BMPs were the most viable path to look into at this point of the research for a height increase technique. The studies and research have shown that this type of protein, which is in the family of TGF-β cellular proteins is very effective in spinal fusions of fractures.
Source 1 – Title “Intradiscal administration of osteogenic protein-1 increases intervertebral disc height and proteoglycan content in the nucleus pulposus in normal adolescent rabbits.”
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005 Jan 1;30(1):25-31; discussion 31-2.
An HS, Takegami K, Kamada H, Nguyen CM, Thonar EJ, Singh K, Andersson GB, Masuda K.
Source
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush Medical College at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA.
Abstract
STUDY DESIGN:
A study of the disc height and biochemical changes in the rabbit intervertebral disc after injection of osteogenic protein-1 into the nucleus pulposus.
OBJECTIVES:
To evaluate the in vivo effects of osteogenic protein-1 administered intradiscally to the intervertebral disc of rabbits.
SUMMARY OF BACKGROUND DATA:
Growth factors, such as osteogenic protein-1 and transforming growth factor-beta, have the ability to stimulate synthesis of proteoglycan and collagen in vitro. No attempts have yet been made to determine the effects of these growth factors in an in vivo model.
METHODS:
Twenty-four New Zealand adolescent white rabbits were divided evenly into two subject groups. In one group, three consecutive intervertebral discs were injected with saline; whereas in the other group, they were injected with osteogenic protein-1 in saline. At 2, 4, and 8 weeks after the injection, the intervertebral disc heights of the injected specimens were measured by lateral plain radiographs and compared with preinjection measurements. The change in disc height was expressed as the percent disc height index compared with the preinjection value. After the radiographic measurements were obtained, the intervertebral discs were removed and analyzed for DNA, proteoglycan, and collagen contents.
RESULTS:
At 2 weeks after the injections, the mean disc height index of the osteogenic protein-1-injected discs was 15% greater than that of the saline group. The increase in disc height with osteogenic protein-1 injection was still statistically significant at the 4- and 8-week time points. The proteoglycan content of the nucleus pulposus in discs injected with osteogenic protein-1 was higher than that in the saline group at the 2-week time point. The osteogenic protein-1-induced effect on the proteoglycan content was also present at the 4- and 8- week time intervals; however, these increases were not statistically significant. There were no significant differences in the DNA content, normalized to noninjected control, of the nucleus pulposus between the saline and osteogenic protein-1 groups. However, a significant increase in the DNA content of the anulus fibrosus in the osteogenic protein-1 group, compared with that of the anulus fibrosus in the saline group, was observed after 4 weeks.
CONCLUSION:
To date, no study has demonstrated the potential in vivo effects of growth factors on the intervertebral disc. The present study reports that the intradiscal administration of osteogenic protein-1 in vivo results in an increased disc height present at 2, 4, and 8 weeks and an increase in PG content of the nucleus pulposus at the 2-week time point. Therefore, osteogenic protein-1 may act to stimulate metabolic activity in the nucleus pulposus. Continued research is needed to evaluate the potential of growth factor-induced reversal of age-related disc degeneration in an appropriate animal model. In addition, studies in a nonhuman primate animal model will be essential before considering intradiscal injection of growth factors in humans.
PMID: 15626976 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE]
Source 2 – Title “Osteogenic protein-1 injection into a degenerated disc induces the restoration of disc height and structural changes in the rabbit anular puncture model.”
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006 Apr 1;31(7):742-54.
K, Imai Y, Okuma M, Muehleman C, Nakagawa K, Akeda K, Thonar E, Andersson G, An HS.
Source
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush Medical College at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA. kmasuda@rush.edu
Abstract
STUDY DESIGN:
In vivo study of the effect of injection of osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1) on a rabbit anular needle puncture model of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration.
OBJECTIVE:
To study radiographic, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), biochemical, and histologic changes in the rabbit IVD after injection of OP-1 into the nucleus pulposus in a needle puncture disc degeneration model.
SUMMARY OF THE BACKGROUND DATA:
Growth factors, such as OP-1, have the ability to stimulate synthesis of proteoglycans and collagen in vitro. The in vivo injection of OP-1 into the normal rabbit IVD has increased disc height and proteoglycan content in the anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus. However, to our knowledge, no attempts have yet been made to determine the effects of these growth factors in an in vivo model of disc degeneration.
METHODS:
New Zealand adolescent white rabbits (n = 90, 8 for baseline evaluation, 82 at 8 times) received an anular puncture in 2 noncontiguous discs with an 18-gauge needle to induce disc degeneration. Four weeks later, either 5% lactose (10 microL) or OP-1 (100 microg in 10 microL 5% lactose) was injected into the center of the nucleus pulposus. The disc height was followed radiographically for up to 24 weeks after the injections. At the 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24-week times after the injection, rabbits were euthanized, and MRI of the harvested spinal columns was obtained to grade the degeneration. The discs injected with OP-1 or lactose and noninjected discs were subjected to biochemical and histologic analysis. The specimens at the 24-week time were limited to histologic evaluation.
RESULTS:
The anular puncture with a needle induced a consistent disc narrowing within 4 weeks. The injection of OP-1 induced a restoration of disc height at 6 weeks, which was sustained for the entire experimental period, up to 24 weeks after the injection. The injection of lactose alone did not change the course of disc narrowing over the same time. MRI grading score showed significant differences between the OP-1 and lactose groups at the 8, 12, and 24-week times, suggesting an increase in water content in the nucleus pulposus of the OP-1 group. The proteoglycan content of the nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus was significantly higher in the OP-1 group than in the control group. The degeneration grades of the punctured discs in the OP-1 group were significantly lower than those in the lactose group.
CONCLUSION:
The results of this study show the feasibility of restoring degenerative rabbit discs by a single injection of OP-1 into the nucleus pulposus. Importantly, the effects of the OP-1 injection on disc height were sustained for up to 24 weeks. The metabolic changes in the cells, following a single injection, might be sustained and, thus, induce long-term changes in disc structure. An efficacy study in large animals is required to show further that the intradiscal injection of OP-1, or bone morphogenetic proteins or growth factors with similar properties would be useful for the structural restoration of the IVD in humans.
PMID: 16582847 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE]
Source 3 – Title “Restoration of disc height loss by recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 injection into intervertebral discs undergoing degeneration induced by an intradiscal injection of chondroitinase ABC.”
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 May 15;32(11):1197-205.
Restoration of disc height loss by recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 injection into intervertebral discs undergoing degeneration induced by an intradiscal injection of chondroitinase ABC.
Imai Y, Okuma M, An HS, Nakagawa K, Yamada M, Muehleman C, Thonar E, Masuda K.
Source<
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Rush Medical College at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL 60612, USA.
Abstract
STUDY DESIGN:
In vivo study of the effect of an injection of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 into degenerated discs induced by chondroitinase ABC.
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate the efficacy of an injection of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 to induce the recovery of disc height, and biochemical and histologic repair, in discs degenerated through enzymatic digestion by chondroitinase ABC.
SUMMARY OF THE BACKGROUND DATA:
Chondroitinase ABC is currently proposed as a chemonucleolysis agent; however, postchemonucleolysis degeneration is currently unavoidable. Recombinant human OP-1 has been shown to promote extracellular matrix repair in vitro and in vivo.
METHODS:
Fifty-four adolescent New Zealand white rabbits were used. Four weeks after an initial injection of chondroitinase ABC (10 mU/disc), 5% lactose (10 microL/disc) or recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 (100 microg in 10 microL lactose/disc) was injected. Disc heights were monitored radiographically at 2-week intervals, and rabbits were killed at 6, 8, 12, and 16 weeks after the initial chondroitinase ABC injections. The intervertebral discs were subjected to histologic and biochemical analyses.
RESULTS:
Significant disc space narrowing was observed in both groups 2 weeks after the injection of chondroitinase ABC. In the chondroitinase ABC/lactose group, this narrowing progressed after the vehicle injection and was sustained for up to 16 weeks. In the chondroitinase ABC/recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 group, the disc height index showed a significant increase at 6 weeks (lactose vs. recombinant human osteogenic protein-1; P < 0.01); this recovery was sustained for up to 16 weeks. The proteoglycan content was higher in the chondroitinase ABC/recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 group than in the chondroitinase ABC/lactose group. However, histologic changes, after the recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 injection, were not observed.
CONCLUSIONS:
A single injection of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 into a rabbit disc dramatically reversed the decrease in disc height induced by chondroitinase ABC chemonucleolysis. The recovery was significant and sustained over the next 12 weeks. The therapeutic effects of both chondroitinase ABC chemonucleolysis and recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 injections should be further explored in higher animals before it is applied to humans.
PMID: 17495776 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE]
Me: Tyler from HeightQuest wrote a similar article HERE about the studies which shows the effects of using OP-1 aka BMP-7 on the intervertebral disk height.
What I am not sure of is the first passage which he takes. are the subjects in the experiment rabbits, sheep, or humans?? However, the results are very clear. using GDF-5 (I have got to do a post about this compound protein!!) and OP-1 injected into the disks increased the nucleus pulpous cell types and the collagen, which suggest less compression in the vertebrate area (thus more height, even if it is only a few millimeters) and more elasticity.
His next section about the sheep show incredible results which showed that growth plates were increased from using recombinant OP-1. I quote this passage “”…treatment with rhOP-1 initiated a complex response that was both chondrogenic and osteogenic in nature”
The next part shows that the BMP-7/OP-1 also leads to Collagen type II and Proteoglycan synthesis increase so this protein is absolutely critical. I am willing to bet that getting the mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into chondrocytes will only assist in the bone formation process.
Conclusion: This is one of those articles that comes out that creates a whole new pathway to look at and pushes the possibility go height increase further along. With this type of study, I am willing to bet that scientific researchers will find a way to increase height in adult within 10-15 years if they are willing to take some big risks and try a few dangerous experiments on human subjects. The next article will be a complete and full explanation of the facts and information found here. The results are amazing.