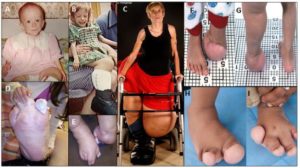
Akt1 overgrowth tends to create proportional overgrowth whereas CNP overgrowth tends to create lankier overgrowth
Mosaic overgrowth with fibroadipose hyperplasia is caused by somatic activating mutations in PIK3CA.
“The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT signaling pathway is critical for cellular growth and metabolism. Correspondingly, loss of function of PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K, or activating mutations in AKT1, AKT2 or AKT3 have been found in distinct disorders featuring overgrowth or hypoglycemia. We performed exome sequencing of DNA from unaffected and affected cells from an individual with an unclassified syndrome of congenital progressive segmental overgrowth of fibrous and adipose tissue and bone and identified the cancer-associated mutation encoding p.His1047Leu in PIK3CA, the gene that encodes the p110α catalytic subunit of PI3K, only in affected cells. Sequencing of PIK3CA in ten additional individuals with overlapping syndromes identified either the p.His1047Leu alteration or a second cancer-associated alteration, p.His1047Arg, in nine cases. Affected dermal fibroblasts showed enhanced basal and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP(3)) generation and concomitant activation of downstream signaling relative to their unaffected counterparts. Our findings characterize a distinct overgrowth syndrome, biochemically demonstrate activation of PI3K signaling and thereby identify a rational therapeutic target.”
Proteus syndrome, a progressively deforming regional overgrowth syndrome that affects bones, adipose, and other mesenchymal tissues, is caused by a somatic p.Glu17Lys AKT1 mutation which constitutively activates PI3K/AKT signaling”
The Overgrowth can be local:
Interesting that in one case ” Muscle is replaced by fibrous and adipose tissue with occasional residual muscle fibers (arrow)”. So muscular tissue basically dedifferentiated. Maybe the same thing could happen with bone and allow neo growth plate formation.
“somatic occurrence of both AKT2 and AKT3 p.Glu17Lys mutants, paralogous to the Proteus-associated AKT1 mutation, have been described.”
Muscular loading may influence Akt1 signaling in bone:
“The cell specific detection of enzyme activation in response to the physiological contractile load within muscle-tendon-bone unit is essential for understanding of the mechanical forces transmission from muscle cells via tendon to the bone{Are these mechanical forces transmitted via fluid flow or by some other means?}. The hypothesis that the physiological mechanical loading regulates activation of Akt1/PKBalpha at Thr308 and at Ser473 in muscle fibers within muscle-tendon-bone unit was tested using quantitative immunohistochemistry, confocal double fluorescence analysis, and immunoblot analysis. In comparison to the staining intensities in peripheral regions of the muscle fibers, Akt1/PKBalpha was detected with a higher staining intensity in muscle fibers at the myotendinous junction (MTJ) areas. In muscle fibers at the MTJ areas, Akt1/PKBalpha is dually phosphorylated at Thr308 and Ser473. The immunohistochemical results were confirmed by immunoblot analysis. We conclude that contractile load generated by masticatory muscles induces local domain-dependent expression of Akt1/PKBalpha as well as activation by dually phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473 in muscle fibers at the MTJ areas within muscle-tendon-bone unit.”
“The muscle-tendon-bone unit contains myocytes, fibroblasts, nerve fibers, blood vessels, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and extracellular matrix.”
“Tendons transmit forces generated from muscle cells at the muscle-tendon-junction (MTJ) to bone cells.”
“Full activation of Akt1/PKBα requires phosphorylation of the enzyme at Thr308 and at Ser473”
“Thr308 is phosphorylated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1). The phosphorylation of Akt1/PKBα at Ser473 is mediated by both mammalian target of rapamycin-rictor complex (mTORC2) and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) depending on type of stimulus.”
“muscle fibers apply forces to the bone cells via tendon cells, which arise from a specialized region called the MTJ. In the MTJ, myofibrils and collagen fibers overlap, forming longitudinal infoldings”
According to The role of Akt1 in terminal stages of endochondral bone formation: angiogenesis and ossification., Akt1 may be involved in regulating MMP14 levels and Akt1 deficient mice had a delay in the formation of secondary ossificiation centers.
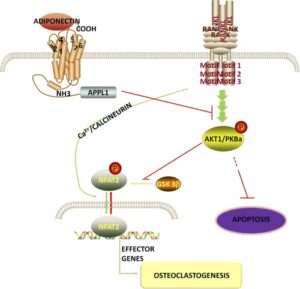
According to Adiponectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via APPL1-mediated suppression of Akt1., Akt may reulate osteoclastgenesis. So Akt1 may play a role in growth by increasing bone turnover.
So Akt1 increases Osteoclastogenesis and decreases Osteoclast Apoptosis.
Homocysteine may be an Adiponectin inhibitor according to Inhibition of adiponectin production by homocysteine: a potential mechanism for alcoholic liver disease.